Look Great.
Feel Great. Be Great.
Experience tailored nutrition designed just for you. Our personalized care plans prioritize your unique needs, ensuring the best path to recovery and wellness.
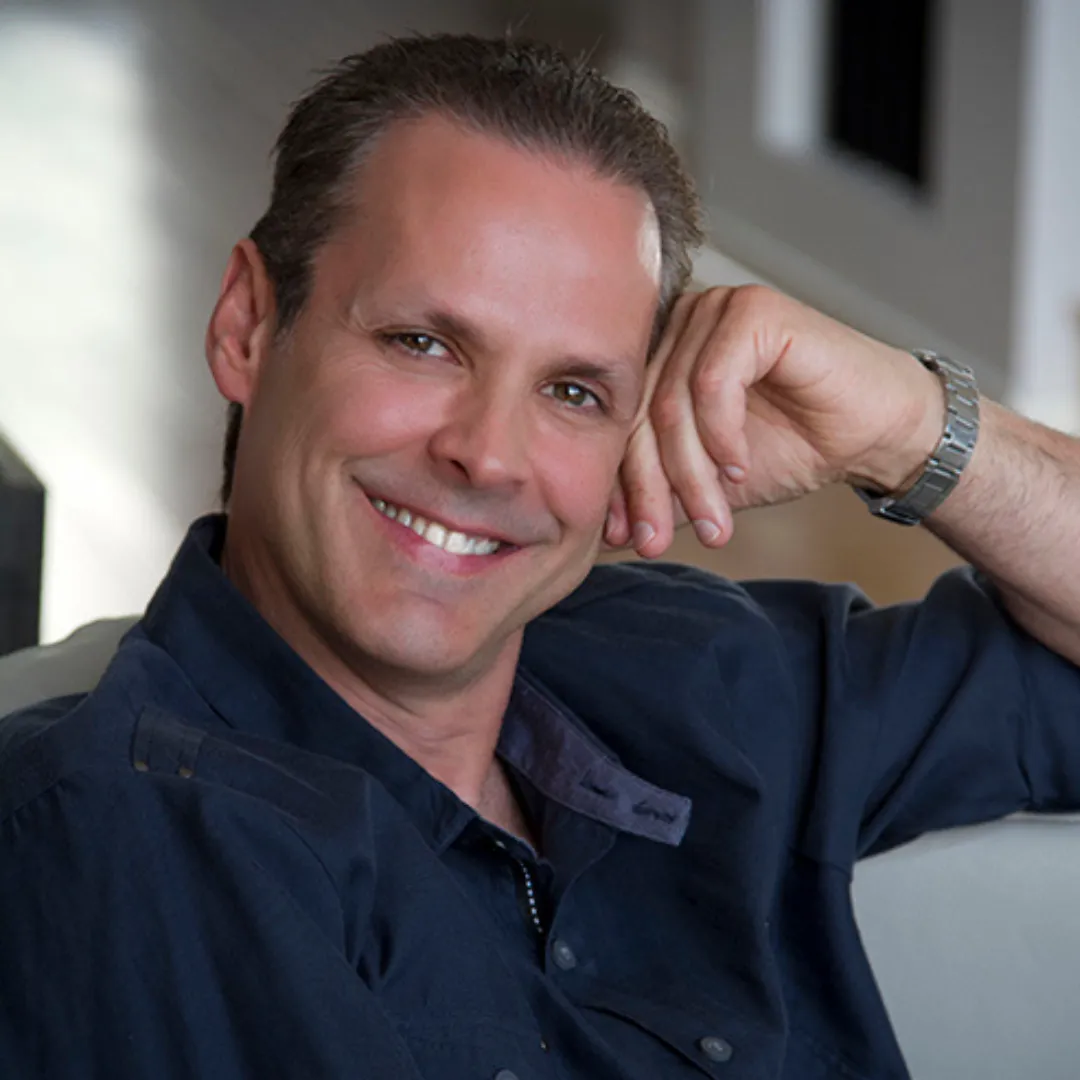

David Allen
Celebrity Nutritionist
David Allen is the trusted expert whom top celebrities, business leaders, athletes, and individuals striving for peak performance rely on for assistance. We adopt a comprehensive method to thoroughly evaluate a client’s present health condition and provide cutting-edge therapies to enhance your life and performance. Coupled with our concierge approach to nutrition and healing, we ensure tailored care that addresses the unique needs of each client.
Services
Concierge Wellness Consultants

David Allen's concierge wellness consultancy offers personalized, convenient wellness solutions for celebrities, top professionals, athletes, and health-conscious individuals. With hands-on care and bespoke plans, David ensures optimal health and personalized attention for every client.


Ongoing Support & Wellness Plans

At David Allen Nutrition, we offer comprehensive, ongoing nutrition and wellness plans tailored to your needs. Guided by David and supported by our expert nutrition staff, we create personalized diet and wellness plans to help you reach your desired goals, from weight loss and anti-aging to managing health disorders and overall wellness. Our team is dedicated to keeping you on track, providing continuous support, innovative therapies, and adjustments to ensure optimal wellness.
Sports Nutrition
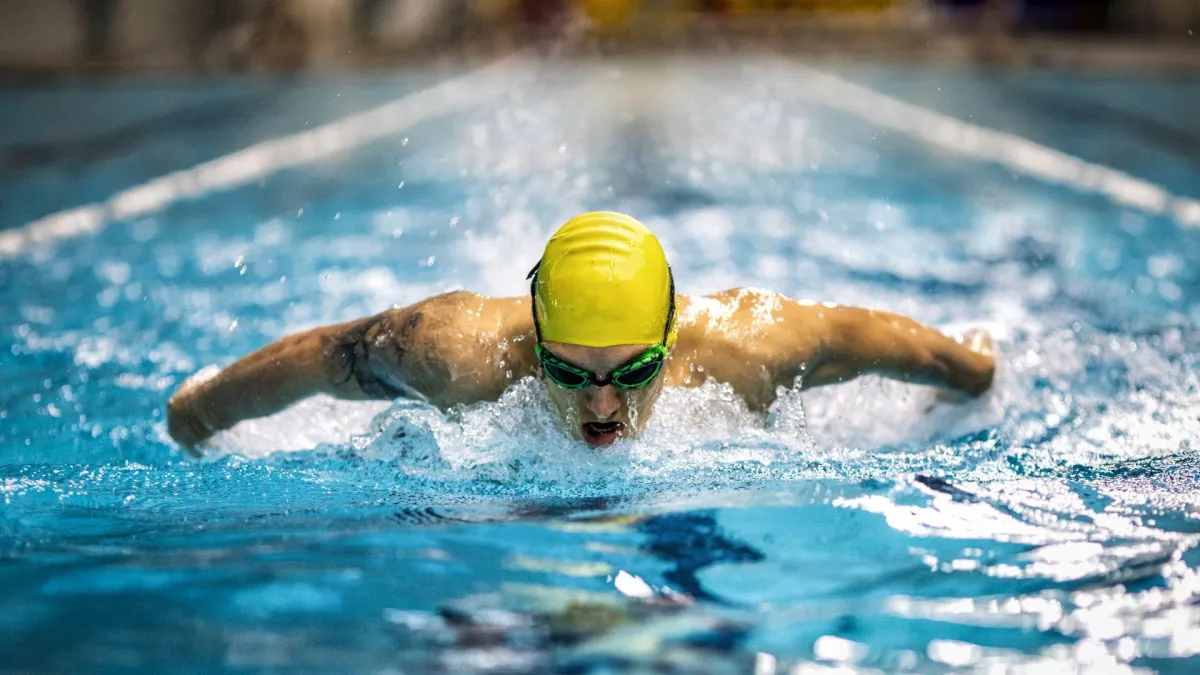

David Allen's sports nutrition services are designed to optimize athletic performance and recovery. We work with top athletes to provide tailored nutrition plans and expert guidance, ensuring they receive the precise nutrients and support needed to excel in their sport and maintain peak physical condition.
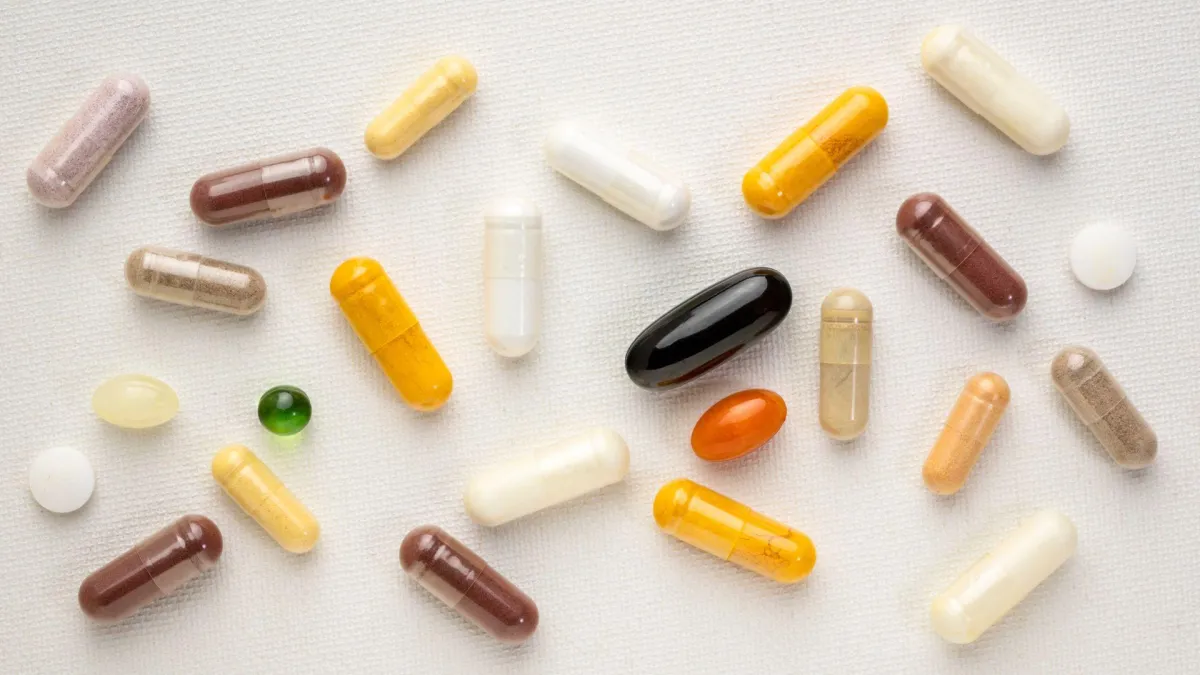


Suppliment Support

At David Allen Nutrition, we offer proprietary and specifically designed supplements and nutraceuticals to support your health goals. Our team creates individualized and customized supplement packs tailored to each client's unique needs, ensuring optimal health and wellness through targeted nutritional support.
David Allen Signature Products
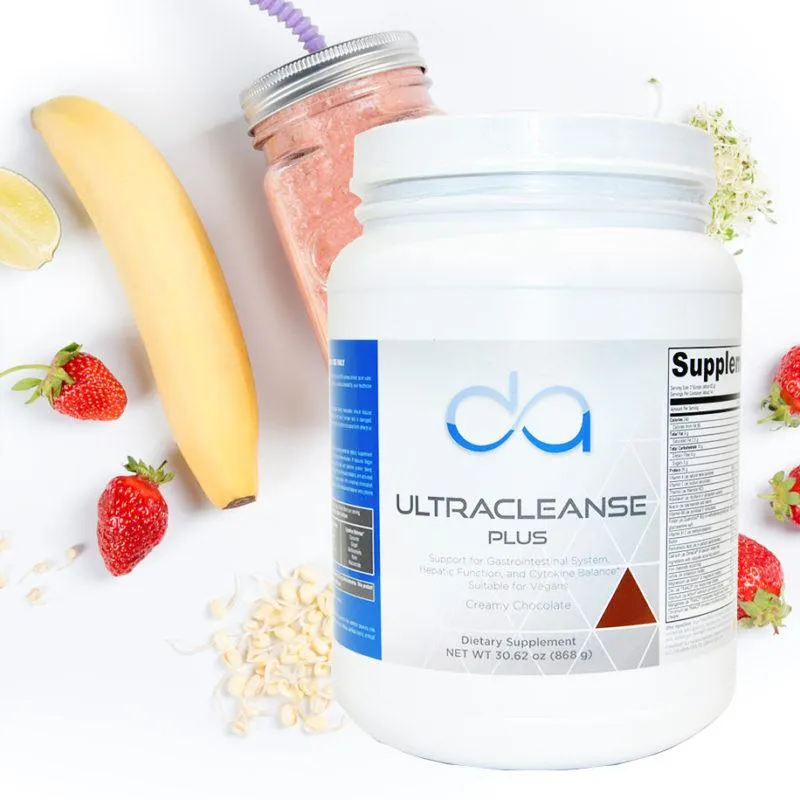

David Allen Cleanses
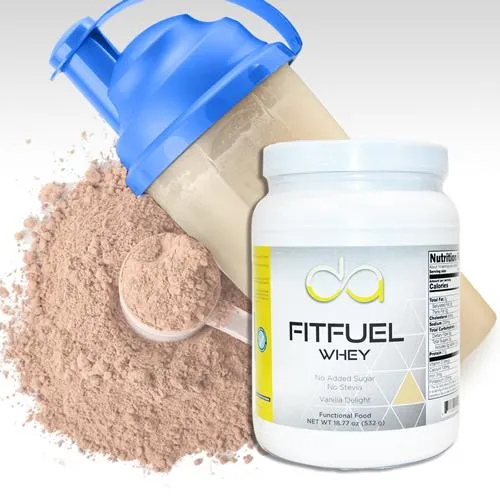

David Allen Protein Powders

David Allen Supplements
Our Team

David Allen
Founder

Drew Prinz
Clinical Nutritionist

Tanya Lyle
Nutritionist
FAQS
What happens during the first appointment?
In the first appointment, you will meet with David Allen. This initial consultation provides you with the opportunity to discuss your nutrition and wellness concerns in detail. David will take the time to understand your unique needs and will recommend the best path forward to help you achieve your health and wellness goals.
Do I have to be in Los Angeles to meet with David?
No, you do not have to live in Los Angeles to meet with David. Appointments can be conducted via Zoom, phone, or in our office in Woodland Hills, offering flexibility no matter where you are located.
Will I need to have blood work or other testing done?
You might need blood testing, and we offer various options to accommodate your needs. You can either use your blood testing options through your insurance or take advantage of our in-house or mobile blood testing facility. If testing is needed, we will communicate the available options to you and help you choose the best one for your situation.
Do you offer ongoing support?
Yes, we offer ongoing support. Our relationship with you is built on personalized care, crafted specifically to meet your individual needs. We can develop an individualized plan tailored to your unique health and wellness goals. Some clients require ongoing support, and we are committed to providing the continuous guidance and assistance you need to achieve and maintain optimal health.
Are my appointments covered under insurance?
No, appointments are not covered under insurance.
If I need supplements, can you ship them to me?
Yes, we can ship supplements to you. We offer next-day or two-day shipping via UPS anywhere in the United States. For international clients, we provide a variety of international shipping options. Additionally, we offer a messenger service for clients located within the Los Angeles area.

Get In Touch
Email: [email protected]
Phone: (818) 887-2720
Address Office: 6324 Canoga Avenue #150, Woodland Hills CA 91367
Assistance Hours:
Monday – Friday 9:00 AM to 5:00 PM
© Copyright 2025 | All Rights Reserved - David Allen Nutrition
Privacy Policy Terms & Conditions Cookie Policy Acceptable Use